来源
Spring中获取request的几种方法,及其线程安全性分析
概述
在哪里使用
1)在Spring的Bean中使用request对象:既包括Controller、Service、Repository等MVC的Bean,也包括了Component等普通的Spring Bean。为了方便说明,后文中Spring中的Bean一律简称为Bean。
2)在非Bean中使用request对象:如普通的Java对象的方法中使用,或在类的静态方法中使用。
此外,本文讨论是围绕代表请求的request对象展开的,但所用方法同样适用于response对象、InputStream/Reader、OutputStream/ Writer等;其中InputStream/Reader可以读取请求中的数据,OutputStream/ Writer可以向响应写入数据。
最后,获取request对象的方法与Spring及MVC的版本也有关系;本文基于Spring4进行讨论,且所做的实验都是使用4.1.1版本。
研究手段
客户端测试代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String prefix = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "") + "::";
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
final String value = prefix + i;
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:8080/test?key=" + value);
httpClient.execute(httpGet);
httpClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
}
|
服务器中Controller代码如下(暂时省略了获取request对象的代码)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @Controller
public class TestController {
public static Set<String> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<>();
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
String value = request.getParameter("key");
if (set.contains(value)) {
System.out.println(value + "\t重复出现,request并发不安全!");
} else {
System.out.println(value);
set.add(value);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
|
补充:上述代码原使用HashSet来判断value是否重复,经网友批评指正,使用线程不安全的集合类验证线程安全性是欠妥的,现已改为ConcurrentSkipListSet。
Controller中加参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test(HttpServletRequest request) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
|
该方法实现的原理是,在Controller方法开始处理请求时,Spring会将request对象赋值到方法参数中。除了request对象,可以通过这种方法获取的参数还有很多,具体可以参见:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-ann-methods
Controller中获取request对象后,如果要在其他方法中(如service方法、工具类方法等)使用request对象,需要在调用这些方法时将request对象作为参数传入。
线程安全性
测试结果:线程安全
分析:此时request对象是方法参数,相当于局部变量,毫无疑问是线程安全的。
优缺点
这种方法的主要缺点是request对象写起来冗余太多,主要体现在两点:
1)如果多个controller方法中都需要request对象,那么在每个方法中都需要添加一遍request参数
2)request对象的获取只能从controller开始,如果使用request对象的地方在函数调用层级比较深的地方,那么整个调用链上的所有方法都需要添加request参数
实际上,在整个请求处理的过程中,request对象是贯穿始终的;也就是说,除了定时器等特殊情况,request对象相当于线程内部的一个全局变量。而该方法,相当于将这个全局变量,传来传去。
自动注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Controller
public class TestController{
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
|
测试结果:线程安全
分析:在Spring中,Controller的scope是singleton(单例),也就是说在整个web系统中,只有一个TestController;但是其中注入的request却是线程安全的,原因在于:
使用这种方式,当Bean(本例的TestController)初始化时,Spring并没有注入一个request对象,而是注入了一个代理(proxy);当Bean中需要使用request对象时,通过该代理获取request对象。
下面通过具体的代码对这一实现进行说明。
在上述代码中加入断点,查看request对象的属性,如下图所示:
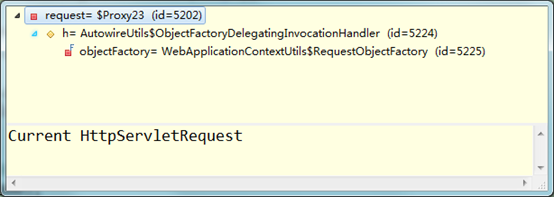
在图中可以看出,request实际上是一个代理:代理的实现参见AutowireUtils的内部类ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory;
public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
|
手动调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
|
测试结果:线程安全
分析:该方法与方法2(自动注入)类似,只不过方法2中通过自动注入实现,本方法通过手动方法调用实现。因此本方法也是线程安全的。
优点:可以在非Bean中直接获取。缺点:如果使用的地方较多,代码非常繁琐;因此可以与其他方法配合使用。









